
Intangible outcomes might be recognition, praise, or a sense of achievement. Tangible outcomes include salary and job security. Outputs are what the employee receives from the employer and can also be tangible or intangible. Inputs include time spent working and level of effort but can also include less tangible contributions such as loyalty, commitment, and enthusiasm. Inputs are the employee’s contribution to the workplace. Accordingly, equity structure in the workplace is based on the ratio of inputs to outcomes. Adams, a workplace and behavioral psychologist, asserted that employees seek to maintain equity between what they put into a job and what they receive from it against the perceived inputs and outcomes of others.Įquity theory proposes that people value fair treatment, which motivates them to maintain a similar standard of fairness with their coworkers and the organization. Regarded as one of many theories of justice, equity theory was first developed in 1963 by John Stacey Adams.
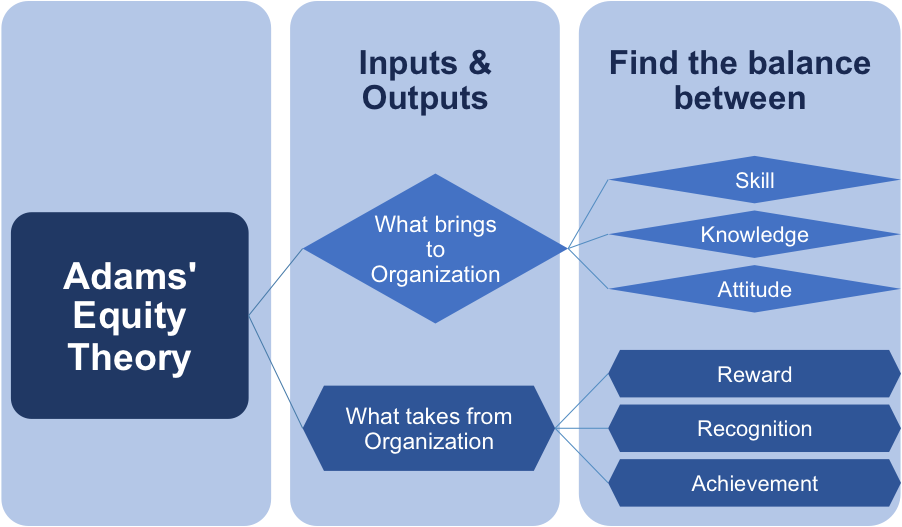
Individuals analyze their environment, develop reactions and feelings, and respond in certain predictable ways.Įquity theory attempts to explain relational satisfaction in terms of perceived fairness: that is, people evaluate the extent to which there is a fair or unfair distribution of resources within their interpersonal relationships.

In contrast to the need-based theories we have covered so far, process-based theories view motivation as a rational process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
